Your guide to hardware, use cases, research, AI-powered coaching, and more
As L&D innovators explore opportunities to leverage immersive learning for just-in-time, flow-of-work solutions, they’ve got more questions than ever about the design, development, implementation, and effectiveness of these solutions.
Below are some of the most frequently asked questions we’ve been hearing from L&D leaders in a wide range of industries and organizations. We’ve mixed in audience questions from our live Tech Talk with Training Industry on January 13th and a few FAQs from our innovative client-partners.
1. How might we overcome hygiene and cost concerns about headsets?
Let’s first level-set and clarify that when we’re talking about headsets, we mean a virtual reality (VR) headset that immerses the wearer in a fully digital, 360-degree 3D environment that they experience instead of the real world.
Some ways to help with hygiene concerns include:
- Disposable covers, similar to face masks, which create a barrier between the face and the headset.
- Hand sanitizer stations, which are often offered at conferences and events.
- Sanitization stations for larger deployments, allowing for quick and easy disinfection of headsets.
- The use of augmented reality (AR) as an alternative, where participants scan a code on their smartphones or tablets to experience the solution without utilizing a shared device. They then experience digital content as a layer on top of their real environment. (The “view in room” feature on many shopping websites is a great example of AR!)
Because participants use their own devices to enter the experience, an AR solution can also help alleviate cost concerns associated with VR hardware. So can WebXR, a browser-based immersive technology that can be experienced via headset or via browsers on a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. WebXR can be a great option for any organization to alleviate cost or hygiene concerns—or simply to offer their people options for how to consume the experience.
2. How do you create a 3D environment, and what is the experience like for learners?
Here’s an answer you’ll hear a lot: It depends on the client’s needs!
We have a skilled team of 3D technical artists who create realistic 3D environments by collaborating closely with clients to accurately depict machinery, equipment, and workspaces.
For clients who need a hyperrealistic, extremely precise 3D digital twin of their workspace, our team visits the space with specialized equipment to measure each item and the space itself.
For client projects that don’t need a fully custom environment, we can leverage stock 3D assets that can be adjusted, edited, and customized. This option helps us increase efficiency while reducing cost.
The results? A fully interactive 3D environment where learners can:
- Manipulate objects: Open valves, pick up items, and interact with the environment.
- Experience full-body immersion: Practice skills in an authentic, immediate 3D environment.
- Enjoy a safe practice space: For skills that learners can’t afford to get wrong—yet need to practice—a 3D environment provides a safe environment to try, receive feedback, and try again.
WebXR, the browser-based immersive technology we mentioned in Question 1, can be a great way to scale these benefits to a geographically distributed audience. If learners enter via headsets, they can enjoy the fully immersive digital experience; if they enter via their laptop or tablet, they experience a deeply engaging, realistic experience much like a first-person video game.
3. Are there any efficacy studies showing that VR training outcomes meet or exceed those of job shadowing, classroom training, or traditional eLearning?
There are a few! Below are some findings that have caught our attention.
A comprehensive study of VR training outcomes by PwC found that:
- Learners trained in VR develop soft skills 4x faster than learners trained in the classroom and feel 275% more confident applying what they learned.
- Learners trained in VR are 3.75 times more emotionally connected to the content than classroom learners and 4x more focused than eLearning participants.
The Imperial College of London used VR to train surgeons and discovered that 83% of learners were ready to perform procedures with little guidance after training—compared with an astounding 0% using traditional methods.
A randomized clinical trial focusing on pathology recognition and complex procedural skills found that orthopedic surgeons trained in VR demonstrated “superior learning efficiency, knowledge, and skill transfer” compared with those trained via traditional methods.
The Miami Children’s Health System found that medical staff who learned new procedures in an immersive environment had an 80% retention rate one year later, compared to 20% one week later using traditional training methods.
Why is VR so effective for learning?
- Consistency: VR provides a standardized learning experience, unlike shadowing, where individual mentors may have different teaching styles and levels of experience.
- Repetition: VR allows for repeated practice, which is often impractical with shadowing due to time constraints and mentor availability.
- Safety: VR allows for training on dangerous or rare situations that cannot be replicated through shadowing.
- Scalability: VR enables a global workforce to be trained quickly and efficiently without scheduling conflicts or mentor availability issues. (Browser-based immersive technology WebXR, which learners can access via either a headset or their laptop, tablet, or smartphone, extends the benefits of scalability even further.)
True, an immersive learning strategy is an investment, but it’s a sound one: VR training has been shown to be more cost-effective at scale than traditional classroom or eLearning experiences.
- At 375 learners, VR training achieves cost parity with classroom learning.
- At 1,950 learners, VR training achieves cost parity with eLearning.
- At 3,000 learners, VR training becomes 52% more cost-effective than classroom learning.
4. How do bandwidth and internet connectivity impact the usability of an immersive learning experience?
Native VR applications are pre-downloaded and installed on a headset, making them great for offline access. Of course, you need connectivity for the initial download and any updates but, after that, the experience can run without any internet connectivity.
Because it’s stored and accessed from a server, AR content depends on continuous cellular or internet connectivity. The same goes for WebXR content: Because it’s accessed either via headset or web browser, it relies heavily on internet connection and speed.
Striking a balance between scalability and bandwidth can be complex—and we consult closely with our client-partners to understand their audience, their technical constraints, and their performance objectives.
If you’re curious what an immersive learning solution could look like for your organization, we’ll work with you to design a strategy that works for you. We have extensive experience creating native VR, AR, and WebXR experiences, and even dual-delivery solutions that offer the best of both worlds.
5. What tools do you use to build your immersive simulations?
We’re technology-agnostic, which means that we recommend solutions built with the software, game engines, hardware, and platforms that best fit your needs and technology ecosystems. For example, we leverage game engines like Unity to enable interactions with 3D objects and environments in VR and AR experiences; we often use PlayCanvas for WebXR solutions. These tools offer us the flexibility to create highly immersive, game-like simulations rather than linear eLearning-style experiences.
6. Can accessibility features be built into immersive learning experiences to accommodate learners with different visual, auditory, and mobility abilities? What are some best practices for accessible immersive learning?
We often hear questions about designing XR experiences to meet or exceed WCAG standards; however, these standards speak more to webpages and eLearning. By prioritizing inclusive design and integrating assistive technologies, XR can better serve users with diverse abilities, ensuring a more accessible and beneficial experience for neurodiverse and differently abled learners.
To ensure that we’re designing an XR program or experience that welcomes all learners, we consider a range of accessibility needs across three main areas:
Visual Accessibility: XR typically relies heavily on visual elements, but incorporating audio cues, haptic feedback (such as vibrating hand controls), and robust voice control—which allows learners to talk their way through the experience—can make an immersive experience more inclusive.
Mobility and Interaction Accessibility: Customized controllers, gesture recognition, spatial mapping, and more accessible interactions—such as single-click actions instead of double-clicks—can facilitate smoother interaction and movement.
Cognitive and Linguistic Accessibility: Simplified interfaces, customizable settings (for speed, difficulty, and content complexity), gesture recognition, haptic feedback to offer more guidance on what to do next, and guided tutorials can help improve understanding and engagement with immersive content.
7. How would you incorporate hand movements into an immersive learning experience?
Adding hand movements helps to create a more immersive narrative experience. Hand agency spans a wide range of gestures, including pointing, swiping, pinching, and other refined motor movements that require learners to use their hands instead of controllers.
From simpler tools, such as paintbrushes or wrenches, to highly sophisticated surgical or mechanical tools, hand agency is a great element to leverage for highly specialized, finely detailed interactions. We’ve leveraged hand movements to help learners practice installing and repairing sophisticated machinery and performing specialized medical procedures (See Question 3 for more on why this is effective), to name a few.
That said, hand agency isn’t limited to highly technical use cases: It’s also great in soft skills training to help learners shake hands with an avatar, hold documents, and de-escalate emotionally charged situations.
8. What are some of the most common industries and use cases you see for immersive learning experiences?
Once upon a time, technical training was the dominant use case for immersive learning. Imagine a digital twin of a manufacturing environment where learners could get the hang of specialized equipment, machinery, and procedures—all without harming people or property.
This safe, immersive practice environment speeds learners’ time to proficiency, reduces errors, and enhances retention.
But as we’ve already touched on, as workplaces and job roles continue to evolve and increase in complexity, L&D leaders are embracing XR solutions for a wider spectrum of use cases, including nuanced interpersonal skills like leadership, empathy, and de-escalation. In fact, we’re now seeing a 50-50 split between hands-on technical training and soft skills training use cases.
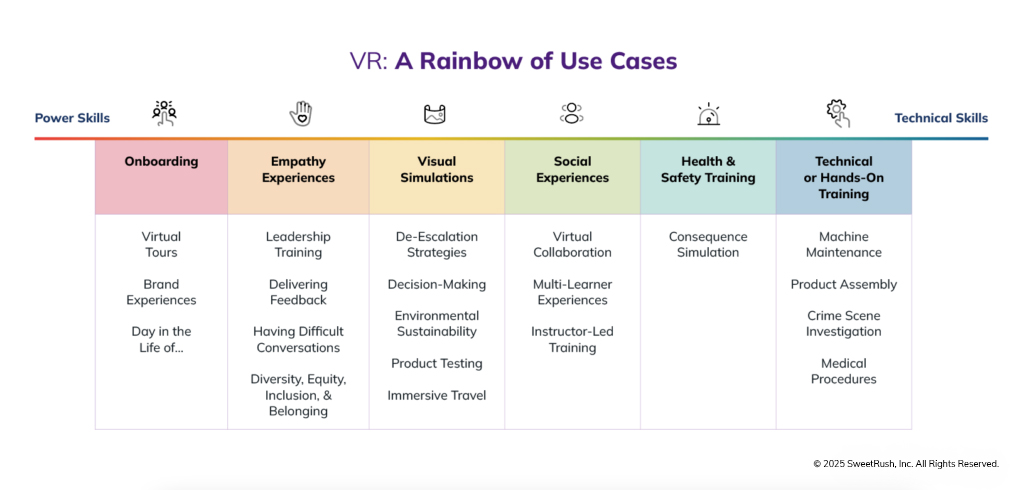
9. I’ve been hearing a lot about incorporating AI into immersive scenarios. Could you share more about how that works and what some use cases might be?
Incorporating generative AI (genAI) into any and all of the immersive learning use cases (see Question 8) helps to increase the emotional immediacy of the learning experience, on-the-job skill transfer, and long-term skill retention…while decreasing learners’ time to competence.
As learners interact with genAI-powered characters, coaches, and scenarios, situations evolve in response to what they say and do. There’s no “script”: Any scenario or interaction can—and does!—unfold in myriad possible ways.
Caveat: Like any team member, genAI works best when it has a clear understanding of its role and purpose.
It’s not a substitute for humans, but it can, with careful oversight, help us extend human expertise and intelligence. (Think of it as a bright, eager, but extremely literal robot assistant that needs constant training and supervision.)
Thanks to its coachability and bottomless energy, genAI can be an effective and engaging addition to our immersive learning solutions. To help learners practice the skills they need, we can train it to serve in any of the following roles:
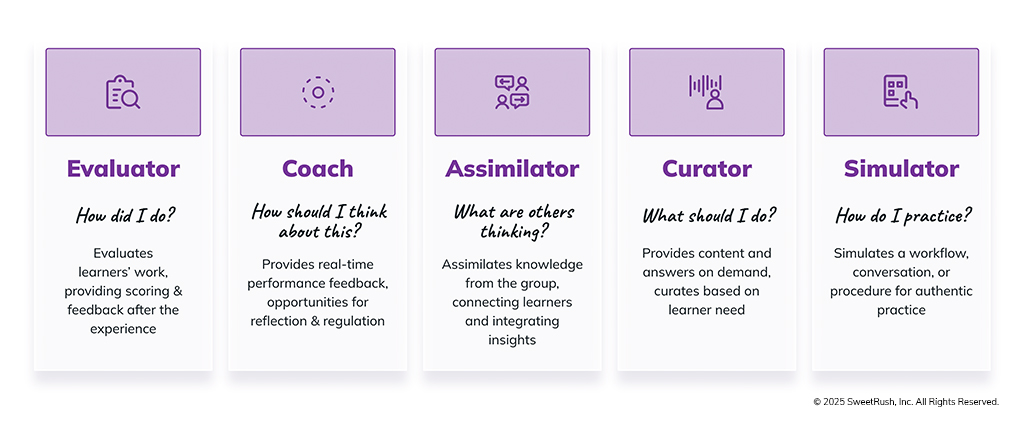
Just like our human team members, genAI also needs to be trained: Context, role, and goals are key. Equally, it needs a personality, backstory, and communication style that feels authentic, not mechanical. Getting our genAI evaluator, coach, assimilator, curator, or simulator to perform well in its role requires plenty of training—complete with trial, error, feedback, and refinement.
GenAI should never stand alone: It’s part of a much larger digital strategy that comprises data security, ethics, privacy, value, authenticity, and commitment to unwavering human oversight. (Discover the foundations and blueprinting of a sound genAI strategy with our comprehensive playbook.)
(Wondering what a genAI-powered coaching experience might look, sound, and feel like? Check out Hilton’s genAI-powered, immersive guest service training experience for its global family of hotel team members.)
10. I’d love to add immersive experiences to my learning portfolio, but I need to work within my organization’s LMS. What options do I have?
This is a very common constraint, and we’ve got a fix for it! It’s called the WebXR LMS Integration Tool, or LIT. Its superpower is integrating easily with your LMS platform to allow WebXR experiences to launch directly from your LMS—helping you create a one-stop shop for all of your learning solutions.
Thanks to LIT, WebXR experiences can launch directly from existing eLearning courses. At launch, LIT cues learners to choose their device: headset or computer.
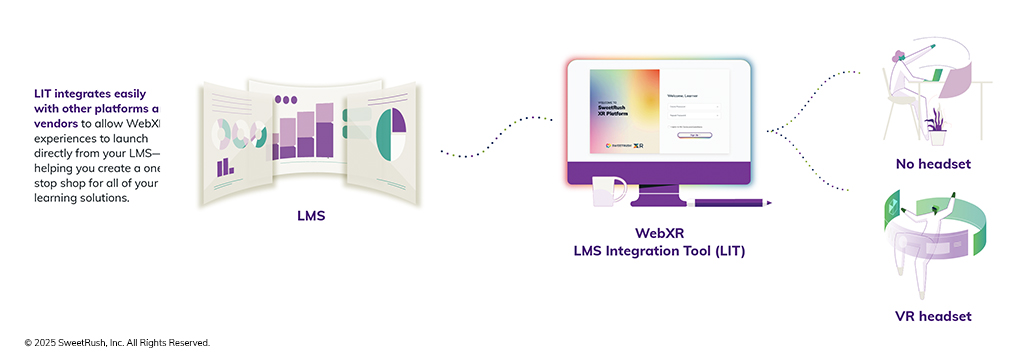
After selecting their devices, learners proceed seamlessly into the WebXR experience. While they’re in the immersive experience, LIT “recognizes” them and brings their performance metrics back to your LMS, creating a continuous, seamless experience on the front and back ends.
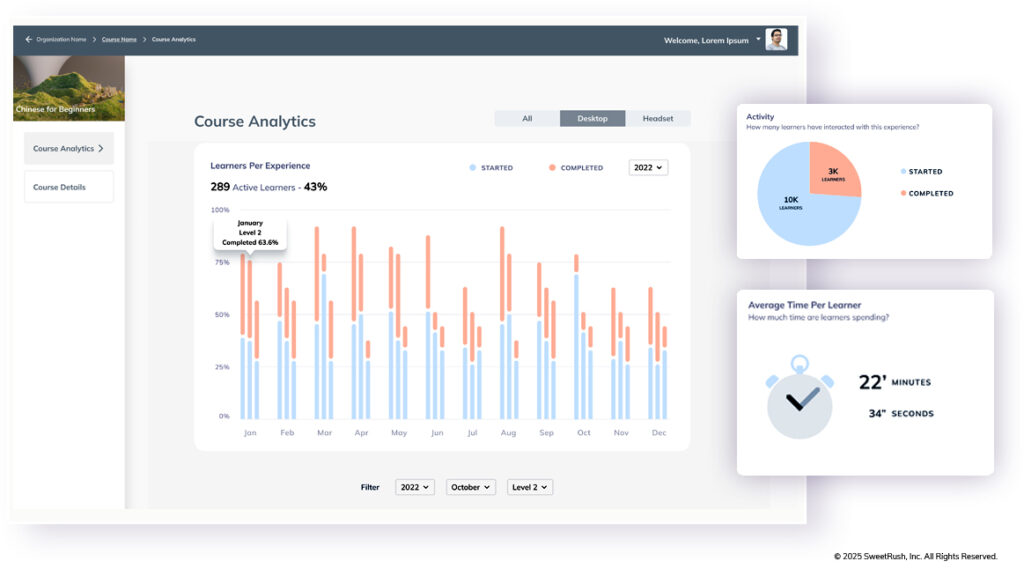
Which data does it collect? That depends on your needs! We work with you to determine the learner performance data that matter most to you—including complex performance data that your LMS may not be able to process. Using our LIT Analytics Dashboard, we can capture and display such detailed learner metrics as tone-of-voice analytics, gaze tracking, and reaction time.
If you’re wondering whether LIT is compatible with your organization’s LMS, our working answer would be “yes”! We’ve deployed WebXR content on hundreds of LMSs, all with their own complexities, quirks, and security protocols.
Got an LMS challenge, immersive or otherwise? Our in-house Director of Systemic Solutioning, John Cleave, would love to hear more about your current learning and IT ecosystem and how we might help you build, in the words of one client-partner, “with, through, over, around, and under” your existing environment.
11. Questions about immersive learning and AI strategy?
Wondering how immersive learning solutions for a variety of use cases might look, sound, and feel? Check out the webisode featuring no fewer than eight real-life immersive simulations we’ve created with some of our most innovative client-partners. (Yes, AI is involved!)
If you’ve got a question of your own about immersive learning and AI strategies, technologies, or scaling, we’re all ears! We’re incredibly excited about fresh opportunities to bring these effective, engaging, and high-quality experiences to new learner audiences, and we’d love to chat about the possibilities.




